X linked recessive inheritance pdf
it is an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked trait. In some cases, students picked a “trait” such as wearing glasses. Since the purpose of this was to focus on identifying the pattern,
Get PDF (91K) Options for accessing this content: If you are a society or association member and require assistance with obtaining online access instructions please contact our …
5.2.4 X-linked recessive (XR) Because males have only one X-chromosome, any male that inherits an X-linked recessive disease allele will be affected by it (assuming complete penetrance). Therefore, in XR modes of inheritance, males tend to be affected more frequently than females in a population.
Sex chromosome linked diseases jump to x-linked dominant sex linked inheritance pdf inheritance genes on the x or y chromosome are called sex-linked.For example, sex sex linked inheritance examples chromosome linked diseases an x-linked recessive allele in humans causes haemophilia.
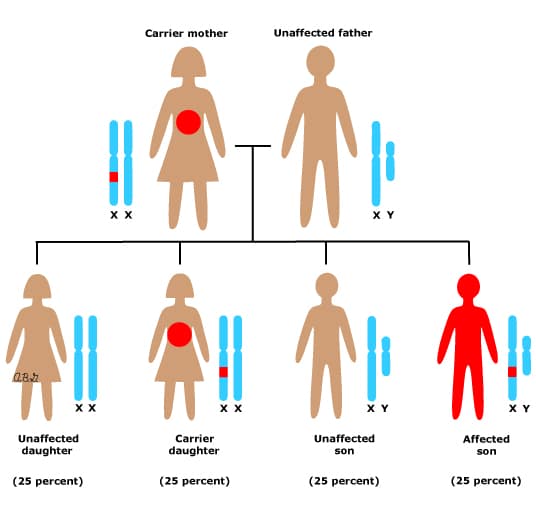
For a carrier female of an X-linked recessive disorder having children with a normal male, each son has a 1 in 2 (50%) chance of being affected and each daughter has a 1 in 2 (50%) chance of being a carrier.
Sex(X)-linked Recessive Inheritance Ask students to assign a genotype for each individual in the pedigree by writing it on the blank line below the circle or square. With this type of inheritance we use the symbols X and Y in the genotype to represent the sex …
Monarch Phenotype: X-linked recessive inheritance (HP:0001419)
Sex-linked diseases are passed down through families through one of the X or Y chromosomes. X and Y are sex chromosomes. Dominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent causes disease, even though the matching gene from the other parent is normal.
The term “carrier” is usually reserved for a female who is a carrier but CANNOT have symptoms such as in an X-linked recessive disease. When a gene mutation spontaneously occurs in a family for the first time rather than by inheritance, it is called a de novo mutation.
Called x-linked traits.If an x-linked trait is recessive, females have a 1 in 3 chance of inheriting that trait.Males have a 1 in 2 chance of inheriting that trait.For this reason, these recessive phenotypes are more often.2 pedigrees and sex-linked traits.
Inheritance of Sex-linked Characteristics •Thomas Hunt Morgan –first to explain –White eyes in Drosophila Fig 4.12. Fig 4.12 Locus for eye colour is X-linked Males are hemizygous. Fig 4.12 Reciprocal cross. Reciprocal crosses –produced different results in F1 and F2-consistent with X-linked inheritance Fig 4.12. Non-disjunction Chromosomes fail to separate in anaphase 1 –non
When you consider X-linked inheritance, perhaps you thought about the fact that males have an X and a Y chromosome and that females have two X’s or maybe even red-green color blindness or hemophilia A came to mind. Those are both X-linked disorders. We will certainly
X-linked recessive inheritance is an inheritance pattern that’s specific for certain genetic variants found on the X chromosome. Since the number of X chromosomes a person has depends on his or her genetic sex, disease-causing variants found in genes on the X chromosome have different implications for males and females. For males (who only have one X chromosome), a single genetic variant is
Hence, to answer the question, an X-linked dominant trait is a dominant characteristic located in the x chromosome, while an X-linked recessive trait is one that is recessive and located in the
Juvenile retinoschisis Conditions – GTR – NCBI

Pedigree Analysis methods dominant recessive and x
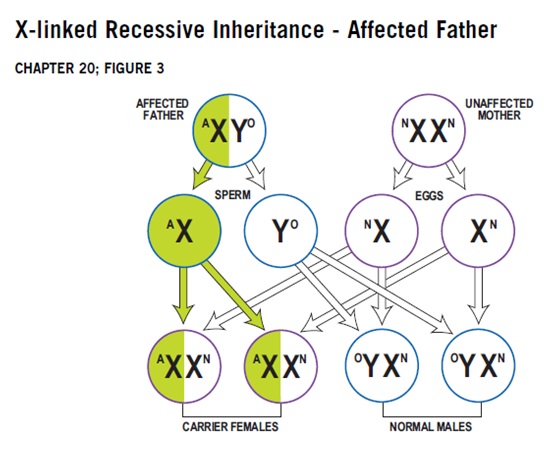
For an X-linked recessive trait… A healthy father cannot have affected daughters. Since he is healthy, his (only) X must have a healthy version of the allele… and since he passes that single X to every one of his daughters, they MUST be healthy (if the trait is recessive, it doesn’t matter what the mother gives since the father is giving the dominant, healthy allele).
Agammaglobulinemia: X-Linked and Autosomal Recessive IDF Patient & Family Handbook 14 The basic defect in both X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia and autosomal recessive agammaglobulinemia is a failure of B-lymphocyte precursors to mature into B-lymphocytes and ultimately plasma cells. Since they lack the cells that are responsible for producing immunoglobulins, these patients have severe
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance X-linked recessive inheritance is designated when phenotypic expression is observed predominantly in males of unaffected, heterozygous mothers. All female offspring of affected males are obligate carriers.
recessive, X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive. X linked recessive b) List all possible genotypes of the following individuals in the pedigree. Individuals Genotypes #1 XR XR or XR Xr #3 XR Xr c) What is the probability of Individual A being affected? The father of Individual A has the genotype XrY. Individual A is a female so she will inherit the Xr from her father. The probability that
Tiziana Granata, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 2012. Menkes disease. This X-linked, recessive disorder, also known as kinky hair disease, is a neurodegenerative disease due to impaired copper transport, resulting in copper deficiency.
16/05/2016 · It explains how to find a pedigree based on characteristics with examples as dominant pedigree, recessive pedigree and x linked pedigree. Dominant inheritance – …
Rules of Inheritance X-Linked Recessive More males than females are affected Affected sons are usually born to unaffected mothers, thus the trait skips generations Approximately 1/2 of carrier mothers’ sons are affected It is never passed from father to son All daughters of affected fathers are carriers Rules of Inheritance Autosomal Recessive Appears in both sexes with equal frequency Trait
X-linked inheritance Some conditions are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome (one of the sex chromosomes). These are usually inherited in a recessive pattern, but in a slightly different way from the autosomal recessive pattern described above.
3/12/2018 · The F8 gene is located on the X-chromosome. Therefore, hemophilia A is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one mutated copy of the F8 gene in each cell is enough to cause hemophilia A.
What is x linked recessive inheritance? The X chromosome has many genes that are important for growth and development. The Y chromosome is much smaller and has fewer genes. Females have two X chromosomes (XX) and therefore if one of the genes on an X chromosome has a change, the normal gene on the other X chromosome can compensate for the changed copy. If this happens the female …

PDF This study determined the family history and clinical features that suggested autosomal recessive rather than X-linked Alport syndrome. All patients had the diagnosis of Alport syndrome and
X-linked recessive inheritance X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome .
18/12/2018 · X-linked recessive X-linked recessive disorders are also caused by mutations in genes on the X chromosome. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition.
This disorder generally occurs as a hered itary syndrome with X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. However, autosomal dominant or recessive and sporad ic …
genetic inheritance known as X-linked dominant inheritance. In summary Genes contain the instructions for growth and development. Some gene changes make the gene faulty so that the message is not read correctly or is not read at all by the cell. A variation in a gene that makes it faulty is called a mutation An X-linked dominant gene is a gene located on the X chromosome and effects males and
X-Linked Inheritance. Traits that are determined by alleles carried on the X chromosome are referred to as X-linked. X-linked alleles require a specific notation: X c or X + where the “+” represents the dominant allele and the lowercase letter the recessive allele.
Single Gene Disorders polymorphism
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance X-linked recessive disease usually occurs in males who have inherited a recessive X-linked mutation from their mother. Rarely, the disease may be seen in females who have inherited mutations in the same gene X-linked from both parents. More typically, the mother is a carrier and is unaffected, although it is not uncommon for female carriers of X-linked disorders
X-linked recessive inheritance (A) Normal male X Y X X X Y X X Carrier female Normal female Affected male Normal male Carrier female X-linked recessive inheritance (B)
Inheritance patterns can be autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or X-linked recessive. For many conditions there may even be different mutations in the gene which can cause disease, for example, in cystic fibrosis there are over 200 possible mutations in the gene but they mostly produce the same disease pattern.
A characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons. In X-linked recessive inheritance, a female with one altered copy of the gene in each cell is called a carrier.
Providing research and caregiver resources to the Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy community. Characteristics of X-linked recessive inheritance DuchenneConnect
An autosomal dominant trait is one which manifests in the heterozygous state, i.e. in a person possessing both an abnormal or mutant allele and the normal allele.
Pedigree analysis is an example of abductive reasoning. In pedigree analysis you need to look for any clues that will allow you to decide if the trait is dominant or recessive and whether it is linked to an autosomal chromosome, or to the X chroomsome. On the following page(s) we’ll discuss the reasoning that goes into solving pedigree analysis puzzles. I . II . IV. General Assumptions. In
X-linked recessive inheritance Used to describe a characteristic or condition in which an alteration in one gene on the X chromosome causes the condition in males but not usually when females have one copy of the altered gene.
maternal (X-linked) Table S4: Main clinical characteristics of the patients with pathogenic or probably pathogenic variants, as well as some variants of unknown clinical consequence. Patient
In two families with X-linked recessive inheritance of HED, the condition was severe in females. A critical review of previously reported cases of presumed autosomal recessive HED suggests that an autosomal recessive form of the condition identical to the X-linked HED may not exist. All sporadic instances of females with classic HED should be considered to be X-linked recessive, and … – x acto pencil sharpener manual X-linked Inheritance X-linked recessive inheritance – The incidence of the trait is much higher in males than in females, heterozygous females are usually unaffected. The gene (and trait) is usually transmitted from an affected male to his grandsons through his daughters; the grandsons have a 50% chance of inheriting the trait. Males never transmit the disease directly to their sons, so that
28/05/2014 · X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID) is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. A condition is X-linked if the changed (mutated) gene responsible for the condition is located on the X chromosome.
4. What is the inheritance pattern? X-linked recessive In Pedigree above, which of the following females is least likely to be a heterozygote for the rare X-
Clues for Sex-linked Inheritance Recessive • no father-to-son transmission • predominantly males affected • trait my skip generations 1. For each of the pedigrees below, identify the mode of inheritance and provide at least 2 reasons for your choice. c) d) 2. Below is a pedigree for an inherited lung disease. Provide the genotypes of each of the individuals marked with lower case letters
Here you will find general information about the impact genetics can have on health and the community
X-linked juvenile retinoschisis is characterized by symmetric bilateral macular involvement with onset in the first decade of life, in some cases as early as age three months. Fundus examination shows areas of schisis (splitting of the nerve fiber layer of the retina) in the macula, sometimes giving the impression of a spoke wheel pattern.
been identified with autosomal dominant or X-linked inheritance. Recessive inheritance has been reported in 16% of affected families but so far no disease genes have been identified.1,2 The number of affected individuals is small in most families with the condition, because of incomplete disease penetrance. Therefore, gene identification studies are most often done with a candidate gene
Two families are described in which the Ehlers–Danlos syndrome is apparently transmitted as an X-linked recessive character. The results of tests for the Xg blood groups and for colour vision show that the locus for the Ehlers–Danlos syndrome is not close to that for the Xg groups nor very close to the locus for deutan colour-blindness.
What is the difference between x-linked dominant traits
X-linked recessive inheritance occurs when there is a mutation or deletion affecting one or more genes on the X chromosome. Because a woman has two X chromosomes, even if there is a gene mutation in one copy, the other, normal copy, means that she is not usually severely affected with an X-linked condition. However, the situation is slightly complicated by X inactivation. Normally in cells
X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one X and one Y. Genes on the X chromosome can be recessive or dominant. Their expression in females and males is not the same. X-linked recessive genes are expressed in females only if there are two copies of the gene (one on each X …
PDF We report a pedigree in which six males died of cardiac failure within the first eight months of life. These males were related through healthy females, as with X linked recessive inheritance.
Monogenic Disorders (Single Abnormal Gene) — University of

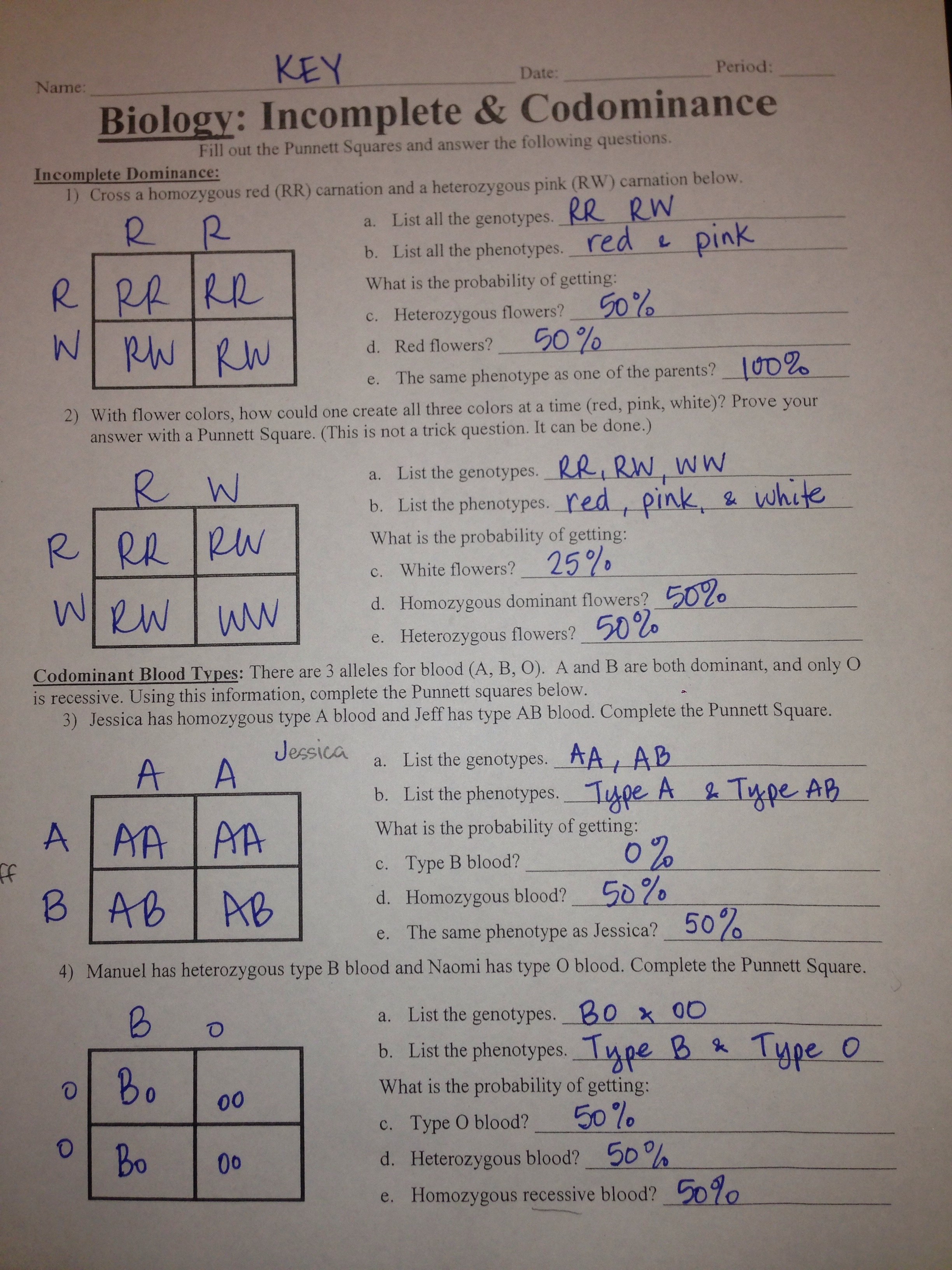
Practice Problems for Genetics Session 3
• Haemophilia is the X linked recessive genetic disorder. It is more common in men than in women. It is more common in men than in women. • Blood normally clots during injuries with in 5 to 10 minutes, depending on the magnitude of the injury.
X-linked Inheritance in Females with Chronic Granulomatous Disease ELAINEL. MILLS, KENNETHS. RHOLL,andPAULG. QUIE,DepartmentofPediatrics, School ofMedicine
Several basic modes of inheritance exist for single-gene disorders: autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, and X-linked recessive. However, not all genetic conditions will follow these patterns, and other rare forms of inheritance such as mitochondrial inheritance exist. (See table at the end of this section.)
a) State the most likely mode of inheritance for this disease. Choose from: autosomal dominant, autosomal Choose from: autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive.
www2.sunysuffolk.edu/kennym/ Pedigree Practice.pdf
Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Dominant and X-linked
Now, you have X-linked inheritance or recessive inheritance covered. How then, let’s consider how a female could be affected by X-linked recessive disorder. We clearly just covered one of them, so we’ll let that one go right away.
In sex-linked inheritance, the gene responsible for the disease is located on the X chromosome. Usually, the abnormal gene is recessive. For these reasons, the resultant disorder is called an X-linked recessive disease. In a woman with such a defective gene, the effects of the abnormal gene are
However, because the gene is X-linked, and because it was the female parent who had the recessive phenotype (white eyes), all the male offspring—who get their only X from their mother—have white eyes (X w Y text X^wtext Y X w Y).
Pedigree Analysis Rules. These pedigree analysis rules are based on the assumption that the disease is rare in the population. When looking at the sex linked inheritance, we will be looking at X linked inheritance patterns.
X linked recessive inheritance. The genes responsible for the trait is located on X chromosome hence called X linked trait. Two copies of a disease allele on the X chromosome are required for an individual with two X chromosomes (a female) to be affected with an X-linked recessive disease.
X-linked conditions are passed down in two ways: X-linked dominant or X-linked recessive. X-linked dominant means that one broken copy of a gene on the X chromosome is …
X-linked recessive inheritance Main article: X-linked recessive inheritance Females possessing one X-linked recessive mutation are considered carriers and will generally not manifest clinical symptoms of …
For recessive traits, males only need one copy of the allele on the X chromosome to display the recessive phenotype, whereas females still need two recessive alleles on both their X chromosomes to have the recessive phenotype. A standard example of such recessive sex-linked inheritance is …
Derivative works of this file: Haemophilia X linked recessive ta.svg This is a retouched picture , which means that it has been digitally altered from its original version. Modifications: Re-Creation as SVG file .
are female and one X and one Y chromosome if we are male. A genetic trait can be dominant or recessive. Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to a trait that is passed from a …
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance – Human Longevity Inc.
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance. Many genetic diseases are caused by changes or “variants” in a single gene. A variant can cause the gene to not work properly. Whether or not people show signs of a genetic disease depends on how the disease is inherited. X-linked recessive inheritance means the disease happens when a variant occurs in a gene located on the X chromosome. Because men only

The Genetics of Cure SMA
Fact Sheet 9 X Linked Recessive Inheritance — Centre for
x trail t31 owners manual – X-Linked Recessive Inheritance UW Staff Web Server
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance Encyclopedia of Special

sex linked pedigree problems pedigree analysis problems
5.2 Inferring the Mode of Inheritance Biology LibreTexts
5.2 Inferring the Mode of Inheritance Biology LibreTexts
X Linked Inheritance ouh.nhs.uk
Derivative works of this file: Haemophilia X linked recessive ta.svg This is a retouched picture , which means that it has been digitally altered from its original version. Modifications: Re-Creation as SVG file .
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance. Many genetic diseases are caused by changes or “variants” in a single gene. A variant can cause the gene to not work properly. Whether or not people show signs of a genetic disease depends on how the disease is inherited. X-linked recessive inheritance means the disease happens when a variant occurs in a gene located on the X chromosome. Because men only
X-linked recessive inheritance Used to describe a characteristic or condition in which an alteration in one gene on the X chromosome causes the condition in males but not usually when females have one copy of the altered gene.
X-linked Inheritance X-linked recessive inheritance – The incidence of the trait is much higher in males than in females, heterozygous females are usually unaffected. The gene (and trait) is usually transmitted from an affected male to his grandsons through his daughters; the grandsons have a 50% chance of inheriting the trait. Males never transmit the disease directly to their sons, so that
X-linked juvenile retinoschisis is characterized by symmetric bilateral macular involvement with onset in the first decade of life, in some cases as early as age three months. Fundus examination shows areas of schisis (splitting of the nerve fiber layer of the retina) in the macula, sometimes giving the impression of a spoke wheel pattern.
X-linked recessive inheritance X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome .
Tiziana Granata, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 2012. Menkes disease. This X-linked, recessive disorder, also known as kinky hair disease, is a neurodegenerative disease due to impaired copper transport, resulting in copper deficiency.
Sex-linked diseases are passed down through families through one of the X or Y chromosomes. X and Y are sex chromosomes. Dominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent causes disease, even though the matching gene from the other parent is normal.
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance X-linked recessive disease usually occurs in males who have inherited a recessive X-linked mutation from their mother. Rarely, the disease may be seen in females who have inherited mutations in the same gene X-linked from both parents. More typically, the mother is a carrier and is unaffected, although it is not uncommon for female carriers of X-linked disorders
Rules of Inheritance X-Linked Recessive More males than females are affected Affected sons are usually born to unaffected mothers, thus the trait skips generations Approximately 1/2 of carrier mothers’ sons are affected It is never passed from father to son All daughters of affected fathers are carriers Rules of Inheritance Autosomal Recessive Appears in both sexes with equal frequency Trait
However, because the gene is X-linked, and because it was the female parent who had the recessive phenotype (white eyes), all the male offspring—who get their only X from their mother—have white eyes (X w Y text X^wtext Y X w Y).
For an X-linked recessive trait… A healthy father cannot have affected daughters. Since he is healthy, his (only) X must have a healthy version of the allele… and since he passes that single X to every one of his daughters, they MUST be healthy (if the trait is recessive, it doesn’t matter what the mother gives since the father is giving the dominant, healthy allele).
Comments
X-linked recessive inheritance occurs when there is a mutation or deletion affecting one or more genes on the X chromosome. Because a woman has two X chromosomes, even if there is a gene mutation in one copy, the other, normal copy, means that she is not usually severely affected with an X-linked condition. However, the situation is slightly complicated by X inactivation. Normally in cells
sex chromosome linked diseases sex linked inheritance pdf
Agammaglobulinemia X-Linked and Autosomal Recessive
16/05/2016 · It explains how to find a pedigree based on characteristics with examples as dominant pedigree, recessive pedigree and x linked pedigree. Dominant inheritance – …
X-Linked Recessive Disorders an overview ScienceDirect
X Linked Inheritance ouh.nhs.uk
X-linked recessive inheritance is an inheritance pattern that’s specific for certain genetic variants found on the X chromosome. Since the number of X chromosomes a person has depends on his or her genetic sex, disease-causing variants found in genes on the X chromosome have different implications for males and females. For males (who only have one X chromosome), a single genetic variant is
The Genetics of Cure SMA
Dominant Inheritance Recessive Inheritance X-linked
Pedigree analysis is an example of abductive reasoning. In pedigree analysis you need to look for any clues that will allow you to decide if the trait is dominant or recessive and whether it is linked to an autosomal chromosome, or to the X chroomsome. On the following page(s) we’ll discuss the reasoning that goes into solving pedigree analysis puzzles. I . II . IV. General Assumptions. In
Fact Sheet 9 X Linked Recessive Inheritance — Centre for
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance UW Staff Web Server
Pedigree Analysis
Monarch Phenotype: X-linked recessive inheritance (HP:0001419)
X-Linked Recessive Diseases HowStuffWorks
This disorder generally occurs as a hered itary syndrome with X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. However, autosomal dominant or recessive and sporad ic …
Monarch Phenotype X-linked recessive inheritance (HP0001419)
X-linked recessive inheritance occurs when there is a mutation or deletion affecting one or more genes on the X chromosome. Because a woman has two X chromosomes, even if there is a gene mutation in one copy, the other, normal copy, means that she is not usually severely affected with an X-linked condition. However, the situation is slightly complicated by X inactivation. Normally in cells
X-linked Patient Library
X linked recessive inheritance (Pedigree analysis
Dominant Inheritance Recessive Inheritance X-linked