X ray crystallography technique pdf
Crystallography is the study of the arrangement of atoms in solids. Before the development of X-ray crystallography, the study of crystals was based on their geometry.
PDF X-ray biocrystallography is the most powerful method to obtain a macromolecular structure. The improvement of computational technologies in recent years and the development of new and
proteins pdf – X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these Sat, 22 Dec 2018 04:37:00 GMT Crystals X Rays And Proteins Comprehensive Protein – A whole account of the
X-ray crystallography explained. X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions.
8/12/2014 · This feature is not available right now. Please try again later.
Elementary Crystallography for X-Ray Diffraction (prepared by James R. Connolly, for EPS400-002, Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction, Spring 2012 (Material in this document is borrowed from many sources; all original material is ©2012 by James R. Connolly)
X-ray crystallography is an imaging technique that uses x-ray diffraction to evaluate the molecular structure of a crystalline solid. This article discusses the critical role played by x-ray crystallography in the elucidation of the structure of DNA.
The first structural biology experiments at an X-ray FEL were performed at soft X-ray energies [3, 4]. At these lower energies (6 keV).
X-ray crystallography is an experimental technique that exploitsthefactthatX-raysarediffractedbycrystals.Itis not an imaging technique. X-rays have the proper
In addition to its sensitivity, the use of crystallography as a screening technique has a number of other advantages over alternative methods. Of key importance is
Download principles of x ray crystallography or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get principles of x ray crystallography book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t worry about it.
Crystallography is the experimental science of the arrangement of atoms in solids. The word The word “crystallography” derives from the Greek words crystallon = cold drop / frozen drop, with its
The determination of crystal structures by X-ray crystallography has come a long way since the 1912 discoveries of von Laue and the Braggs. In the intervening years great advances have been made, so that today it is almost taken for granted that crystal structures can be determined in which hundreds, if not thousands, of sepa rate atomic positions can be found with apparent ease. In the
Download advanced x ray crystallography or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format. Click Download or Read Online button to get advanced x ray crystallography book now. This site is like a library, Use search box in the widget to get ebook that you want.
BECAUSE The underlying principle of function is structure.

x Ray crystallography Request PDF ResearchGate
Despite some similarities and differences, each technique excels where the other falls short, making protein NMR and x-ray crystallography two very complementary spectroscopic methods for high resolution analysis of protein structure and function.
The technique of X-ray crystallography, first used to work out the atomic structure of simple crystals and minerals, is arguably one of the greatest scientific advances of the 20th century. In this lecture Professor Curry will recount the curious origin of the technique (including its Australian roots), explain how it works and discuss how crystallography
X-ray crystallography was the applied method most often used during these studies. The recent award emphasizes the importance of this and similar techniques. The recent award emphasizes the importance of this and similar techniques.
X-ray protein crystallography is a technique by which it is possible to determine the three dimensional positions of each atom in a protein. Now over 100 years old, x-ray crystallography was first used to determine the three dimensional structures of inorganic materials, then small organic molecules, and finally macromolecules like DNA and proteins. To date, about 100,000 protein structures
14/12/2018 · an introduction to x ray crystallography Sun, 16 Dec 2018 14:52:00 GMT an introduction to x ray pdf – Gamma and X-Ray Detection Figure 1.1 Efficiency Calibration
In serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX), protein microcrystals and nanocrystals are introduced into the focus of an X-ray free electron laser (FEL) beam ideally one-by-one in a serial fashion.
The advances in and applications of x-ray and neutron crystallography form the essence of this new edition of this classic textbook, while maintaining the overall plan of the book that has been well received in the academic community since the first edition in 1977. X-ray crystallography is a
Chapter 3 Crystallography and Diffraction Techniques 3.1 General comments on molecular and non-molecular solids Inorganic materials and substances: molecular and non-molecular z Identification of molecular substances—spectroscopic methods and chemical analysis z Identification of non-molecular or crystalline substances—X-ray powder diffraction (and chemical analysis where necessary). Each
from a crystal of copper sulfate [1], X-ray crystallography has been a tremendously invaluable tool in understanding not only the chemical nature of crystals, but also the …
Structural Biology – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Our understanding of life at the molecular level is highly dependent on the ability to map the molecular details of individual proteins and nucleic acids as well as their interactions with each
X-ray crystallography is scientific technique that relies on the diffracted X-rays passing on crystals. It is not an imaging technique. On the basis of diffraction pattern obtained from X-ray scattering off the periodic assembly of molecules or atoms in the crystal, the electron density can be restructure. Usin g electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal, their bonding
X-Ray Crystallography Description. Note that there is NO eating or drinking in the 111-Lab anywhere, except in room 282 LeConte on the bench with the BLUE tape around it.
1 Limitations of x-ray crystallography. From the first crystalline structure determination of table salt in 1914; whose structure elucidation proved the existence of ionic compounds (6), single crystal x-ray diffraction (SC-XRD) has been widening our view of the hidden world of molecular structures.
Science 14 Mar 1975: Vol. 187, Issue 4180, pp. 902-905 DOI: 10.1126/science.187.4180.902-a
In this technique, the pattern produced by the diffraction of the X-rays X-ray crystallography is the most widely used through the closely spaced lattice of atoms in a technique to obtain high-resolution protein crystal is recorded and then analyzed to reveal structural information. It is the study of the nature of that lattice. This technique entails crystals using X-rays. XRC is the primary
Growing and mounting Crystals Your Instrument Will Treasure Richard J. Staples 103/23/2017 X-Ray Crystallography Laboratory Department of Chemistry
X-ray crystallography required the process of exposing a crystal specimen (DNA) to X-rays to determine the locations of the atoms in the “molecules that comprises basic unit of crystal called unit cell”. The task however was not an easy one to attain.
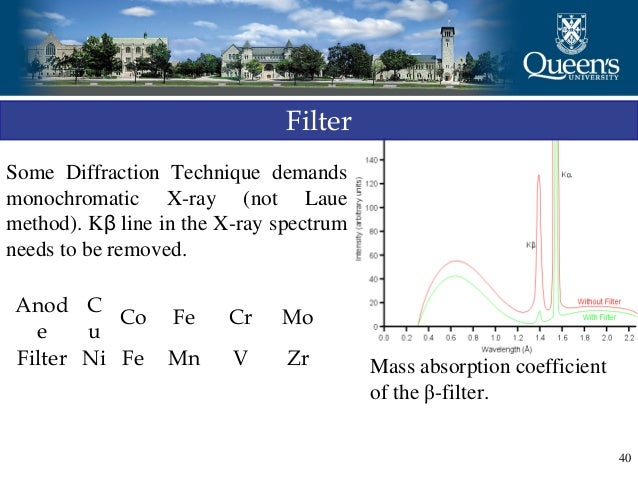
X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X …
X-ray crystallography’s impact is one reason why the UN has called 2014 the International Year of Crystallography. The future is bright . But chemists have a love-hate relationship with X-ray
X-RAY CRYSTALLOGRAPHY INTRODUCTION: X-ray Crystallography is a scientific method of determining the precise positions/arrangements of atoms in a crystal where beams of X-ray strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to diffract into many specific directions OR X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the
Chem 406: Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 7: Structure Determination by X-ray Crystallography I. Introduction A. Most of the structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) were determined by x-ray diffraction. 1. PDB Statistics 2. Other names for x-ray diffraction a. x-ray crystallography b. crystallography B. In the past couple of years there has been a growing number of structures, …
ARCHIVES OF RIOCHEMISTRY AND BIOPHYSICS 161, 533-539 (1972) A Free Interface Diffusion Technique for the Crystallization of Proteins for X-Ray Crystallography
What is X-ray Crystallography ? X-ray crystallography is an experimental technique that exploits the fact that X-rays are diffracted by crystals.
The 10 “must” read book list for X-ray Crystallographers. As I was sitting in my office, at Texas A & M University, pondering where I was going to go for lunch, a student approached and we began a conversation on X-ray
The remarkable success of X-ray crystallography as a means of obtaining high-resolution structural informa-tion about molecules can be attributed to the simple fact that the technique averages over a very large ensemble of identical molecules with identical orientations. The method is inherently immune both to defects in the structure itself and to undesirable perturbations of the physical
Introduction to X-ray crystallography ch.embnet.org
X-ray crystallography is a technique for determining the three-dimensional structure of molecules, including complex biological macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. It is a powerful tool in the elucidation of the three-dimensional structure of a molecule at atomic resolution. Data is collected by diffracting X-rays from a single crystal, which has an ordered, regularly repeating
Overview •X-rays •Crystals •Crystal lattices •Some relevant crystal structures •Crystal planes •Reciprocal lattice •Crystalline and non-crystalline materials
x Ray crystallography is currently the most favoured technique for structure determination of proteins and biological macromolecules. Increasingly, those interested in all branches of the – x ray in pregnancy guidelines
Crystals X Rays And Proteins Comprehensive Protein
Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction FHI

X-ray Crystallography Advanced Lab
X-Ray Crystallography Laboratory Department of Chemistry

(PDF) Protein Structure Determination by X-Ray Crystallography
Basic crystallography UniTrento
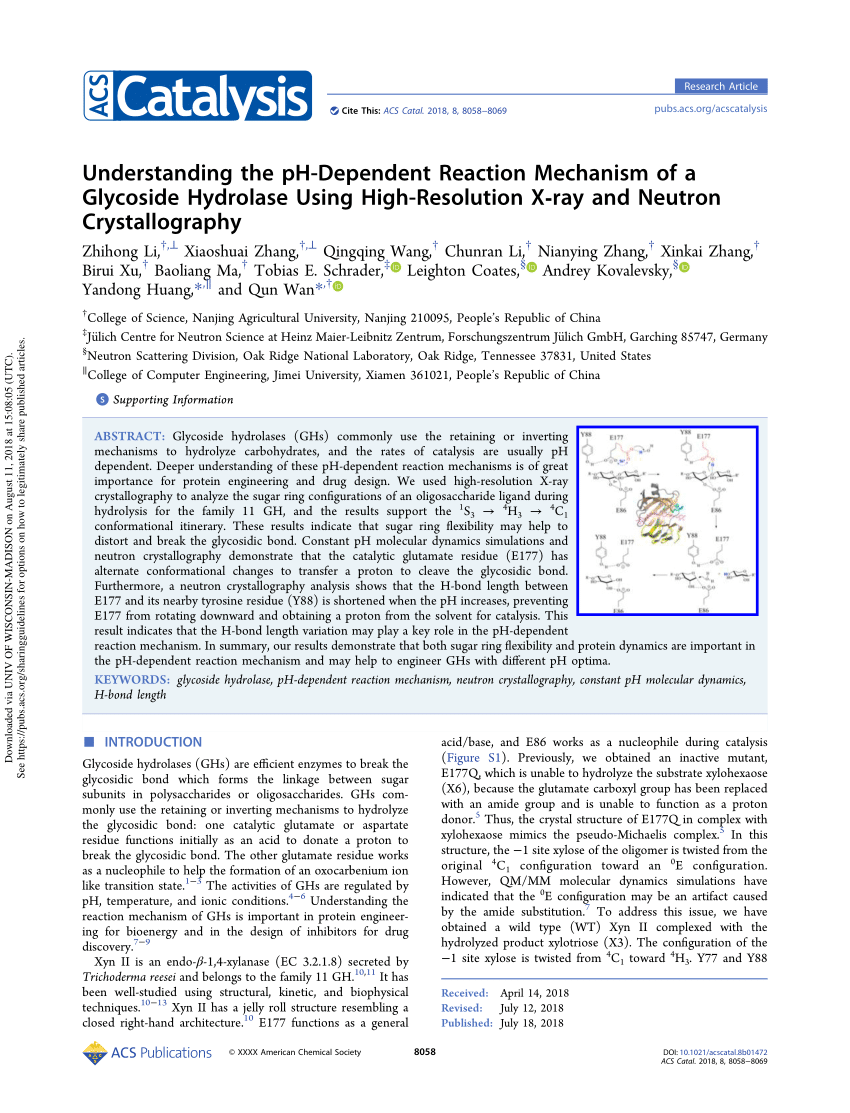
Explainer what is X-ray crystallography? The Conversation
X-ray crystallography explained
– Chapter 3 Crystallography and Diffraction Techniques
Fragment Screening Using X-Ray Crystallography

X-ray crystallography Wikibooks
X-Ray Crystallography and the Elucidation of the Structure
X-ray Protein Crystallography Physics LibreTexts
A Free Interface Diffusion Technique for the
Science 14 Mar 1975: Vol. 187, Issue 4180, pp. 902-905 DOI: 10.1126/science.187.4180.902-a
proteins pdf – X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these Sat, 22 Dec 2018 04:37:00 GMT Crystals X Rays And Proteins Comprehensive Protein – A whole account of the
The remarkable success of X-ray crystallography as a means of obtaining high-resolution structural informa-tion about molecules can be attributed to the simple fact that the technique averages over a very large ensemble of identical molecules with identical orientations. The method is inherently immune both to defects in the structure itself and to undesirable perturbations of the physical
X-ray crystallography explained. X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions.
PDF X-ray biocrystallography is the most powerful method to obtain a macromolecular structure. The improvement of computational technologies in recent years and the development of new and
X-ray crystallography required the process of exposing a crystal specimen (DNA) to X-rays to determine the locations of the atoms in the “molecules that comprises basic unit of crystal called unit cell”. The task however was not an easy one to attain.
In addition to its sensitivity, the use of crystallography as a screening technique has a number of other advantages over alternative methods. Of key importance is
In serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX), protein microcrystals and nanocrystals are introduced into the focus of an X-ray free electron laser (FEL) beam ideally one-by-one in a serial fashion.
The determination of crystal structures by X-ray crystallography has come a long way since the 1912 discoveries of von Laue and the Braggs. In the intervening years great advances have been made, so that today it is almost taken for granted that crystal structures can be determined in which hundreds, if not thousands, of sepa rate atomic positions can be found with apparent ease. In the
Chapter 3 Crystallography and Diffraction Techniques 3.1 General comments on molecular and non-molecular solids Inorganic materials and substances: molecular and non-molecular z Identification of molecular substances—spectroscopic methods and chemical analysis z Identification of non-molecular or crystalline substances—X-ray powder diffraction (and chemical analysis where necessary). Each
In this technique, the pattern produced by the diffraction of the X-rays X-ray crystallography is the most widely used through the closely spaced lattice of atoms in a technique to obtain high-resolution protein crystal is recorded and then analyzed to reveal structural information. It is the study of the nature of that lattice. This technique entails crystals using X-rays. XRC is the primary
x Ray crystallography is currently the most favoured technique for structure determination of proteins and biological macromolecules. Increasingly, those interested in all branches of the
14/12/2018 · an introduction to x ray crystallography Sun, 16 Dec 2018 14:52:00 GMT an introduction to x ray pdf – Gamma and X-Ray Detection Figure 1.1 Efficiency Calibration
X-ray crystallography is scientific technique that relies on the diffracted X-rays passing on crystals. It is not an imaging technique. On the basis of diffraction pattern obtained from X-ray scattering off the periodic assembly of molecules or atoms in the crystal, the electron density can be restructure. Usin g electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal, their bonding
Comments
proteins pdf – X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these Sat, 22 Dec 2018 04:37:00 GMT Crystals X Rays And Proteins Comprehensive Protein – A whole account of the
A Free Interface Diffusion Technique for the
The 10 “must” read book list for X-ray Crystallographers. As I was sitting in my office, at Texas A & M University, pondering where I was going to go for lunch, a student approached and we began a conversation on X-ray
x Ray crystallography Request PDF ResearchGate
X-ray Crystallography Technique Analysis UK Essays
Growing and mounting Crystals Your Instrument Will Treasure Richard J. Staples 103/23/2017 X-Ray Crystallography Laboratory Department of Chemistry
Chapter 3 Crystallography and Diffraction Techniques
Fragment Screening Using X-Ray Crystallography
from a crystal of copper sulfate [1], X-ray crystallography has been a tremendously invaluable tool in understanding not only the chemical nature of crystals, but also the …
Chapter 3 Crystallography and Diffraction Techniques
X-ray crystallography is a technique for determining the three-dimensional structure of molecules, including complex biological macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. It is a powerful tool in the elucidation of the three-dimensional structure of a molecule at atomic resolution. Data is collected by diffracting X-rays from a single crystal, which has an ordered, regularly repeating
X-ray crystallography Wikibooks
X-Ray Crystallography Laboratory Department of Chemistry