X ray diffraction crystallography pdf
Calculates three-dimensional X-ray diffraction patterns for randomly oriented mica (illite) and illite/smectite (I/S) powders with various types and quantities of rotational disorder and composed of two types of randomly interstratified silicate layers.
– Values from Bearden (1967) are reprinted in international Tables for X-Ray Crystallography and most XRD textbooks. • Most recent values are from Hölzer et al. Phys. Rev.
Abstract. x Ray crystallography is currently the most favoured technique for structure determination of proteins and biological macromolecules. Increasingly, those interested in all branches of the biological sciences require structural information to shed light on previously unanswered questions.
Introduction to X-ray diffraction . Introduction to X-ray diffraction describe diffraction vector • Use x (fractional coordinates xyz) instead of r to describe position in real space • It turns out that s·r is equal to h·x (hx+ky+lz) • see web page for details F(h) (x) (ih x)dx cell = ∫ρ exp 2π ⋅ Structure factors and electron density • Turn structure factors back into
The origin of crystallography can be traced to the study for the external appearance of natural minerals, such as quartz, fluorite, pyrite, and corundum, which are regular in shape and clearly
X-ray crystallography and solution scattering experimentssolution scattering experiments Two X-ray diffraction techniques Atomic resolution (0.8 Å -50 nm) Crystallisedform 1 – Macromolecular crystallography Crystallised form Size of macromolecules is limited 2 – Small angle scattering (SAXS) Sample in solution Large macromolecules, assemblies (complexes) Kinetics
Crystallography And Crystal Chemistry An Introduction

Hydrogen atoms can be located accurately and precisely by
This is a refinement program that takes an initial structure, in the form of a crystal structure, for example from a cif file, and refines structural parameters by fitting to PDF data from x-ray or neutron diffraction experiments. It has an easy to use graphical user interface.
X-ray Crystallography is a scientific method used to determine the arrangement of atoms of a crystalline solid in three dimensional space. This technique takes advantage of …
Textbooks on Crystallography. Most textbooks on X-ray diffraction cover basic crystallography. However, these books are useful supplements to learn about some of the more sophisticated aspects.
Home Nanoscience (the study of materials at the nanometer scale) and Nanotechnology (the manipulation of matter at the atomic, molecular and supramolecular scale, aiming at fabricating novel products) have the tangible opportunity of promoting new economical progresses and societal advances.
X- ray Crystallography: Overview – By Dr. Sandhya, Dr. Navin Chandra Gupta and Anshika Tyagi X ray diffraction discloses the relative positions of the atoms in space to determine the stereochemistry. Bond length and distance between atoms can also be calculated by this technique. X- ray diffraction only locates an atom in space and gives an idea of the structure of crystal, but it cannot
X-ray crystallography is a scientific technique that is very similar to medical X-rays. Instead of using an X-ray machine and peering into a person, X-ray crystallography uses X-ray radiation to determine the shape of a molecule that has been crystallized into a solid.
intense X-ray beam and the diffracted X-rays are collected with an area detector (it is advantageous to cool the crystals to low temperatures, primarily to prevent radiation damage) The diffraction pattern consists of reflectiodamage).
Download principles of x ray crystallography or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format. Click Download or Read Online button to get principles of x ray crystallography book now. This site is like a library, Use search box in the widget to get ebook that you want.

X‐ray powder diffraction and crystallography Goals: • Learn how to operate an x‐ray diffractometer. • Index the diffraction peaks from elements with cubic and hexagonal crystal structures.
Crystallography is the most unambiguous method for determining structures of small molecules and macromolecules, and single crystal x-ray diffraction provides accurate and precise measurements of molecular dimensions in a way that no other science can begin to approach.
2 Outline • The History of X-ray • The Principle of X-ray • The Steps towards the 3D structure – Crystallization – X-ray diffraction and data collection
A step-by-step method of teaching the X-ray diffraction analysis of DNA using the approach employed by James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins, Rosalind Franklin, and Raymond Gosling at an upper undergraduate and graduate level is described.
Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction Elena Willinger Lecture series: Modern Methods in Heterogeneous Catalysis Research • Outline •History of X-ray •Sources of X-ray radiation •Physics of X-ray scattering Fundamentals of crystallography •X-ray diffraction methods •X-ray diffraction in material science: examples . History of X-rays Wilhelm Röntgen Anna Bertha Röntgen 1901: The First
Elementary Crystallography for X-ray Diffraction A simplified introduction for EPS 400-002 assembled by Jim Connolly
Protein Crystallography Crystallography-technique reveals the three dimensional structures of molecules by X-ray diffraction. Why X-ray-λ = 1-2 Å, comparable to the C-C bond length of ~1.5 Å
08:59:00 gmt crystallography and crystal chemistry introduction pdf – x-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the Xâ€ray Powder Diffraction And Crystallography – Directory
chemistry introduction pdf – X-ray crystallography is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays Wed, 19 Dec 2018 17:48:00 GMT Crystallography And Crystal Chemistry Introduction To The – • Crystal Structure: Basic Definitions – lecture Crystallography is the experimental
Before the development of X-ray diffraction crystallography (see below), the study of crystals was based on physical measurements of their geometry. This involved measuring the angles of crystal faces relative to each other and to theoretical reference axes (crystallographic axes), and establishing the symmetry of the crystal in question.
This page contains materials for the session introducing crystalline materials. It features a 1-hour lecture video, and also presents the prerequisites, learning objectives, reading assignment, lecture slides, homework with solutions, and resources for further study.
The main selection criteria used to source the x-ray data were that they could, in principle, be obtained in a normally equipped x-ray diffraction laboratory, that the temperature was below 140 K, and that the resolution was at least 0.6 Å. Full details can be found in Materials and Methods as well as in the Supplementary Materials.
X RAY DIFFRACTION • X-Ray Crystallography uses the uniformity of light diffraction of crystals to determine the structure of a molecule or atom. • Then they use an X -ray beam to “hit” the crystallized molecule. The electrons surrounding the molecule diffract as the X-rays hit them. This forms a pattern, this type of pattern is called the X-ray diffraction pattern. PROCEDURE-THE FIRST
X-ray Diffraction Crystallography Home Facebook
Title: Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction Author: Bruker Subject: D8 QUEST and D8 VENTURE are the superior tools for cutting-edge crystallography. From the X-ray source, through the goniometer and detector, to the analytical software they provide the best-in-class solution for your applications.
Identify which planes produce x-ray diffraction peaks in FCC and BCC crystals. Given a graph of x-ray intensity vs. angle, or the 2θ values of the diffraction peaks, determine the crystal structure and lattice constant of the sample.
1 Single Crystal X-Ray Crystallography 1,2 You will use the program APEX2 to determine the structure of an organic compound (to be referred to as Ylid) from the data supplied by our x-ray …
Introduction to X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Learning Activity Basic Theory: Diffraction and Bragg’s Law Take a look at the diagram below: B A. When X-rays interact with a single particle, it scatters the incident beam uniformly in all directions. B. When X-rays interact with a solid material the scattered beams can add together in a few directions and reinforce each other to yield diffraction
X-Ray Diffraction and X-Ray Crystallography Diffraction Diffraction: the various phenomena that are associated with wave propagation (e.g., bending and interference of waves) when the wave passes by an object that disrupts the wave. Diffraction The complex patterns of a diffracted wave result from interference between different rays that traveled to the observer along different paths
Xray Crystallography X-ray Crystallography. Both single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction facilities are available in the School of Chemistry, primarily for researchers within the School of Chemistry but also other Schools in the University.
Elementary Crystallography for X-Ray Diffraction (prepared by James R. Connolly, for EPS400-002, Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction, Spring 2012
Abstract • The goal of this paper is to verify the principles of crystallography at radio-frequencies, and then use the principles to design an antenna. – x sense weather station user manual Crystallography – Defining the Shape of Our Modern World: A Book Exhibit at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Commemorating the 100th anniversary of the discovery of X-ray diffraction…
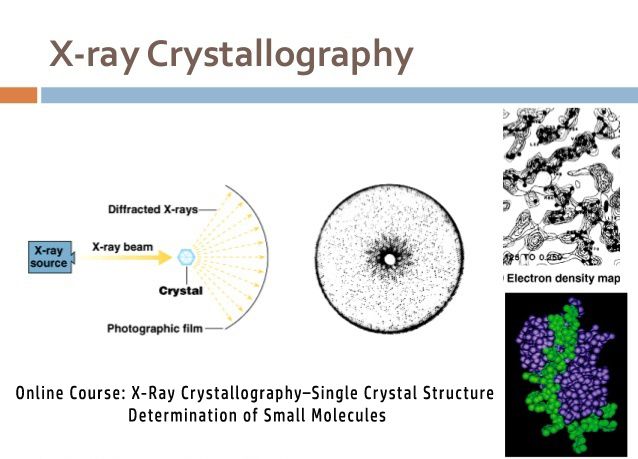
X-RAY CRYSTALLOGRAPHY . X-Ray crystallography is the study of crystal structure by means of X-rays. X-rays are electromagnetic radiations and thus fall into the same class of phenomena as visible light. When a beam of Xrays passes through matter it – is partly transmitted, partly scattered and partly transformed into other forms of energy. The diffraction of X-rays by crystals is a special
14/12/2018 · Stresses by X-ray Diffraction – Click for PDF version. Presenter an introduction to x ray crystallography PDF ePub Mobi Download an introduction to x ray crystallography PDF, ePub, Mobi Books an introduction to x ray crystallography PDF, ePub, Mobi Page 1. an introduction to x ray crystallography Guidelines. Program Notice: The information contained in this PDF is current as of …
10/04/2010 · X-ray crystallography is the primary method for determining the absolute configuration of a molecule and results from crystallographic studies provide unambiguous, accurate, and reliable 3-dimensional structural parameters, which are prerequisites for rational drug design and structure-based functional studies.
Diffraction. Topics Diffraction and wave theory of light Single-slit diffraction Intensity in single-slit diffraction
X-ray crystallography is a form of very high-resolution microscopy which enables the atomic-level visualization of protein structures. Like other forms of microscopy and spectroscopy, x-ray crystallography utilizes electromagnetic radiation to analyze the structure of the protein of interest. Unlike these other forms of structure determination, however, it uses very high energy x-rays (λ ~ 0
Crystallography : Crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystals , in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and diffraction into many specific directions.
For General X-ray Powder Diffraction Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffractometry by Ron Jenkins and Robert L. Snyder (June 28, 1996) ISBN-10: 0471513393
The powder diffraction file, the PDF, THE RIGAKU JOURNAL VOL. 22 / NO. 1 / 2005, 2–15 2 The Rigaku Journal APPLICATIONS OF X-RAY POWDER DIFFRACTION IN THE PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY GREGORY A. STEPHENSON Eli Lilly and Company, Lilly Research Laboratories, Indianapolis, Indiana 46285. E-mail: gas@lilly.com The objective of the following article is to present an overview of the application of X
X-ray Crystallography is a scientific method of determining the precise positions/arrangements of atoms in a crystal where beams of X-ray strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to diffract into many specific directions.
(IUCr) Crystallographic software list
Protein Crystallography Instruct

principles of x ray crystallography Download eBook pdf
X-Ray Diffraction Crystallography Request PDF

x Ray crystallography Molecular Pathology
15. Introduction to Crystallography Crystalline

X-ray Crystallography Vital-IT
Guide to Understanding X-Ray Crystallography UCLA
– Elementary Crystallography for X-Ray Diffraction
University of Glasgow Schools – School of Chemistry

X-Ray Diffraction Crystallography 1st edition
Newmod X-Ray Crystallography Powder Diffraction
X-Ray Crystallography of Chemical Compounds
X-ray Crystallography Vital-IT
X-ray Crystallography is a scientific method used to determine the arrangement of atoms of a crystalline solid in three dimensional space. This technique takes advantage of …
Introduction to X-ray diffraction . Introduction to X-ray diffraction describe diffraction vector • Use x (fractional coordinates xyz) instead of r to describe position in real space • It turns out that s·r is equal to h·x (hx ky lz) • see web page for details F(h) (x) (ih x)dx cell = ∫ρ exp 2π ⋅ Structure factors and electron density • Turn structure factors back into
Before the development of X-ray diffraction crystallography (see below), the study of crystals was based on physical measurements of their geometry. This involved measuring the angles of crystal faces relative to each other and to theoretical reference axes (crystallographic axes), and establishing the symmetry of the crystal in question.
Elementary Crystallography for X-Ray Diffraction (prepared by James R. Connolly, for EPS400-002, Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction, Spring 2012
Xray Crystallography X-ray Crystallography. Both single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction facilities are available in the School of Chemistry, primarily for researchers within the School of Chemistry but also other Schools in the University.
10/04/2010 · X-ray crystallography is the primary method for determining the absolute configuration of a molecule and results from crystallographic studies provide unambiguous, accurate, and reliable 3-dimensional structural parameters, which are prerequisites for rational drug design and structure-based functional studies.
Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction Elena Willinger Lecture series: Modern Methods in Heterogeneous Catalysis Research • Outline •History of X-ray •Sources of X-ray radiation •Physics of X-ray scattering Fundamentals of crystallography •X-ray diffraction methods •X-ray diffraction in material science: examples . History of X-rays Wilhelm Röntgen Anna Bertha Röntgen 1901: The First
Elementary Crystallography for X-ray Diffraction A simplified introduction for EPS 400-002 assembled by Jim Connolly
X- ray Crystallography: Overview – By Dr. Sandhya, Dr. Navin Chandra Gupta and Anshika Tyagi X ray diffraction discloses the relative positions of the atoms in space to determine the stereochemistry. Bond length and distance between atoms can also be calculated by this technique. X- ray diffraction only locates an atom in space and gives an idea of the structure of crystal, but it cannot
Protein Crystallography Crystallography-technique reveals the three dimensional structures of molecules by X-ray diffraction. Why X-ray-λ = 1-2 Å, comparable to the C-C bond length of ~1.5 Å
X-ray crystallography and solution scattering experimentssolution scattering experiments Two X-ray diffraction techniques Atomic resolution (0.8 Å -50 nm) Crystallisedform 1 – Macromolecular crystallography Crystallised form Size of macromolecules is limited 2 – Small angle scattering (SAXS) Sample in solution Large macromolecules, assemblies (complexes) Kinetics
Abstract • The goal of this paper is to verify the principles of crystallography at radio-frequencies, and then use the principles to design an antenna.
Download principles of x ray crystallography or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format. Click Download or Read Online button to get principles of x ray crystallography book now. This site is like a library, Use search box in the widget to get ebook that you want.
Diffraction. Topics Diffraction and wave theory of light Single-slit diffraction Intensity in single-slit diffraction
Identify which planes produce x-ray diffraction peaks in FCC and BCC crystals. Given a graph of x-ray intensity vs. angle, or the 2θ values of the diffraction peaks, determine the crystal structure and lattice constant of the sample.
Comments
A step-by-step method of teaching the X-ray diffraction analysis of DNA using the approach employed by James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins, Rosalind Franklin, and Raymond Gosling at an upper undergraduate and graduate level is described.
D8 Crystallography Solutions Bruker