X ray diffraction technique pdf
Three main diffraction techniques ~ λÅ: X-ray diffraction Electron diffraction Neutron diffraction Principles of X-ray diffraction Single crystal Powder X-rays are passed through a crystalline material and the patterns produced give information of size and shape of the unit cell X-rays passing through a crystal will be bent at various angles: this process is called diffraction X-rays
Review Introduction to Advanced X-ray Diffraction Techniques for Polymeric Thin Films Nicodemus Edwin Widjonarko Department of Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309, USA; nicodemus.widjonarko@colorado.edu
Session II. Advanced Methods in X-ray Powder Diffraction, is designed for the experienced user and focuses on computer-based methods of qualitative and quantitative phase analysis, as well as crystal structure analysis and refinement.
order of diffraction, λ is the x-ray wavelength, d is the lattice spacing of crystal planes, and θ is the diffraction The residual stress determined using x-ray diffraction is angle. For the monochromatic x-rays produced by the the arithmetic average stress in a volume of material metallic target of an x-ray tube, the wavelength is known defined by the irradiated area, which may vary from to
X-ray crystallography (XRC) is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X …
Fluorescence and Powder Diffraction Methods X-ray photons are a form of electromagnetic radiation produced following the ejection of an inner orbital elec- tron and subsequent transition of atomic orbital electrons from states of high to low energy. When a monochro-matic beam of X-ray photons falls onto a given specimen three basic phenomena may result, namely absorption, scatter or
X-ray diffraction is a powerful tool for determining the structure of crystalline materials – this is most often used for identification of unknown samples, such as in geology and earth sciences, or for studying protein structures in life sciences.
the incident X-ray beam, to make the divergence angle of the beam very small, and to obtain high-resolution data, we can obtain diffraction data that are suited to
For example, X-ray spectroscopic technique using a standard crystal diffraction grating is very sensitive in the identification of trace elements; sensitivities of the order of 1 part in 10,000 have been claimed in modern applications to the study of rare earth minerals.
Among the nondestructive methods, the neutron diffraction (ND) and the X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques are widely used for residual stress measurements [8, 9].
(Roentgenstrahlinterferenzen), commonly known as X-ray diffraction (XRD), and was direct evidence for the periodic atomic structure of crystals postulated for several centuries. n l =2dsinq Bragg’s Law. Although Bragg’s law was used to explain the interference pattern of X-rays scattered by crystals, diffraction has been developed to study the structure of all states of matter with any beam
X-ray diffraction is a non-destructive technique to analyse mainly crystalline solids. However, the method can also be utilized to study amorphous or liquid materials. In
X-Ray diffraction technique applied to study of residual
Micro-Analysis X-Ray Diffraction Technique*
This handout provides background on the use and theory of X-ray powder diffraction. Examples of applications of this method to geologic studies are provided. Rocks, sediments, and precipitates are examples of geologic materials that are composed of minerals. Numerous analytical techniques …
X-RAY DIFFRACTION RESIDUAL STRESS TECHNIQUES Paul S. Prevéy, Lambda Research, Inc. GENERAL USES Macrostress measurement • Nondestructive surface residual stress
A method has been developed for obtaining lattice spacings of powder samples by x-ray diffraction in times potentially as short as 1 second. The sample is irradiated with polychromatic radiation from an x-ray tube, and the energy spectrum of x-rays scattered at a given angle is observed with a semiconductor radiation detector, coupled with a
X-ray diffraction (XRD) can provide useful information about the composition of an ore sample in terms of quantification of crystalline phases and also amorphous content. XRD is also a powerful technique for studying substitutional solid solutions that can
X-ray scattering techniques. Jump to navigation Jump to search. This is an X-ray diffraction pattern formed when X-rays are focused on a crystalline material, in this case a protein. Each dot, called a reflection, forms from the coherent interference of scattered X-rays passing through the crystal.

crystals as x-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) analysis. From single-crystal XRD data it is possible to solve and refine the crystalline structure of a new material.
The methodology of stress measurements by X-ray diffraction technique is based on equation of theory of elasticity for deformation in arbitrary direction 7: Where E, ν are elastic constants, φ and ψ are azimuthal and polar angles in spherical coordinate system, σφ are measured stress component in the φ-direction, σ 1 and σ 2 are principal stresses.
crystallography underlying the practice of x-ray diffraction so that the analytical results will rise above the level of a “black box” technique. The first part of the material (including the illustrations) in this section is abstracted from Chapter 3 of Nuffield (1966). The remainder of the material (from Bragg’s Law through the reciprocal lattice) is from Jenkins and Snyder (1996) and
2014; 17(Suppl. 1) X-Ray Diffraction Technique Applied to Study of Residual Stresses after Welding of Duplex Stainless Steel Plates 65 0 ( ) 0 0,,, dd
More appropriately called polycrystalline X-ray diffraction, because it can also be used for sintered samples, metal foils, coatings and films, finished parts, etc.
The Laue techniques works by exposing a crystal to a collimated beam of polychromatic x-rays, and collecting the diffracted image onto a 2D x-ray detector. The image is made up of a number of spots in a pattern, that correspond to the orientation and structure of the crystal. Laue diffraction is widely used in the single crystal industry as a quality measure, as well as academic labs worldwide
In x-ray diffraction, the detector is a transducer that counts the number of photons that collide into it. This photon counter gives a digital readout in number of photons per unit time. Below is a figure of a typical x-ray diffraction unit with all of the parts labeled.
We have used a novel X-ray diffraction technique on the bulk samples of Inconel 625 at different heat-treated conditions to determine the lattice parameters, the lattice misfit of the coherent
Since the discovery of X-rays at the end of the 19th century and the first works on diffraction of X-rays by crystals, huge developments were achieved in the application of …
X-Ray Diffraction. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a nondestructive technique that provides detailed information about the crystallographic structure, chemical …
2 briefly review the basics of diffraction techniques, using laboratory and synchrotron X-ray sources and highlight some of their applications in geoscience.
(PDF) Lattice Misfit Measurement in Inconel 625 by X-Ray
206. X-RAY DIFFRACTION TECHNIQUES DR. S. KRIHM I tmnt to tell you a little bit about the x-ray diffraction of muscle structure. I’m afraid despite your Chairmzn’s remarks, I’m not an expert in
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) X-rays are electromagnetic waves with a wavelength in the range of interatomic distances (0.1-10 Å). This match of length scales makes them suitable for the study of
X-Ray Diffraction Technique 1. X-RAY DIFFRACTION TECHNIQUE 2. What is X-ray diffraction? non-destructive analytical technique for identification and quantitative determination of the various crystalline forms, known as ‘phases’. Identification is achieved by comparing the X-ray diffraction pattern
Revisiting Powder X-ray Diffraction Technique: A Powerful Tool to Characterize Polymers and their Composite Films. Shilpa Kasargod Nagaraj 1, Sachhidananda Shivanna 1, Nithin Kundachira Subramani 1,2 * and Hatna Siddaramaiah 1
The phenomenon of x-ray diffraction from crystals is used both to analyze x-rays of unknown wavelength using a crystal whose atomic structure is known, and to determine, using x-rays of known wavelength, the atomic structure of crystals. As mentioned, it is the second application of x-ray diffraction that will be studied in this experiment. The atomic structure of crystals is deduced from …
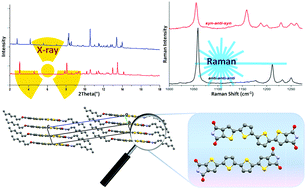
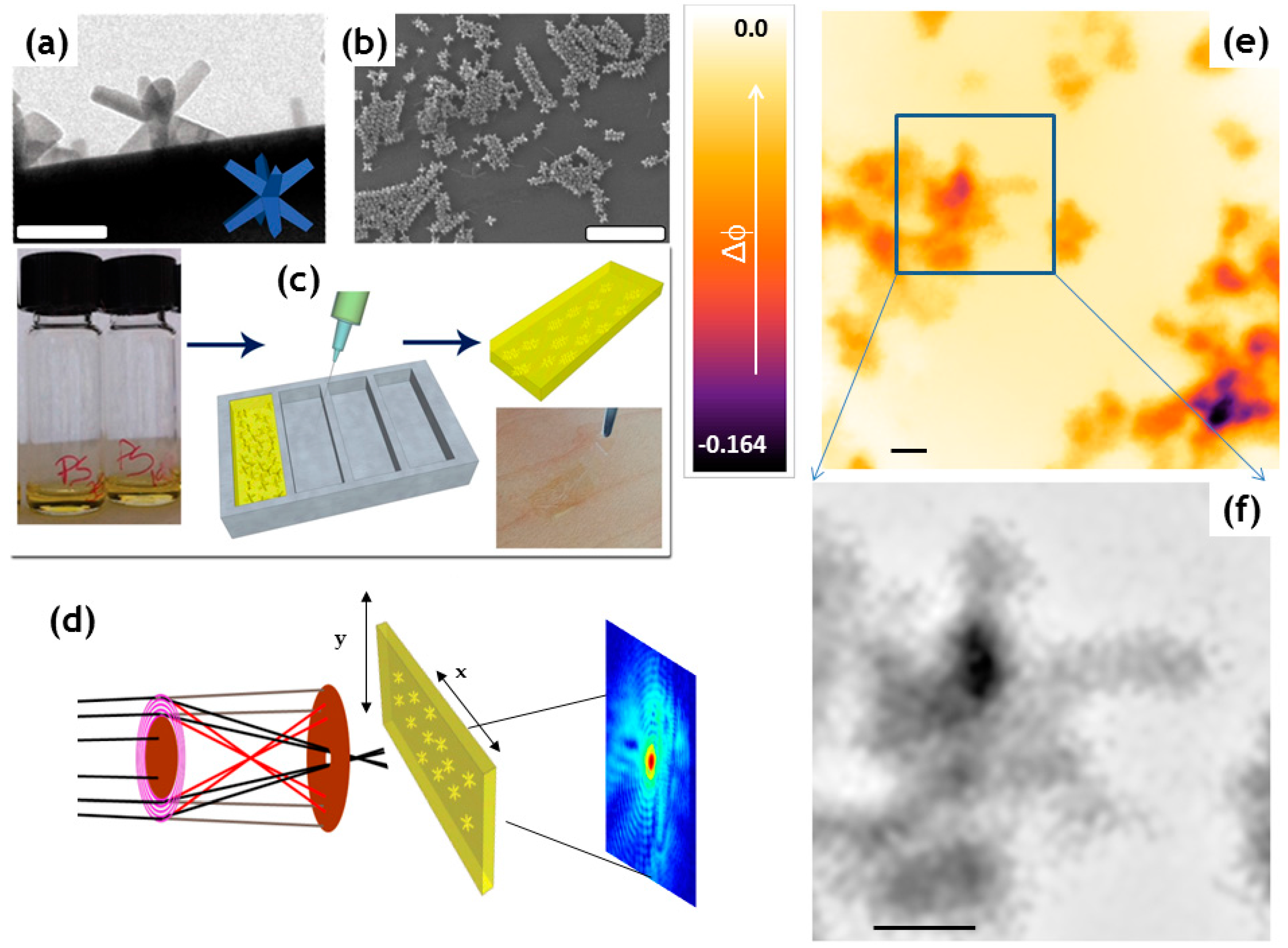
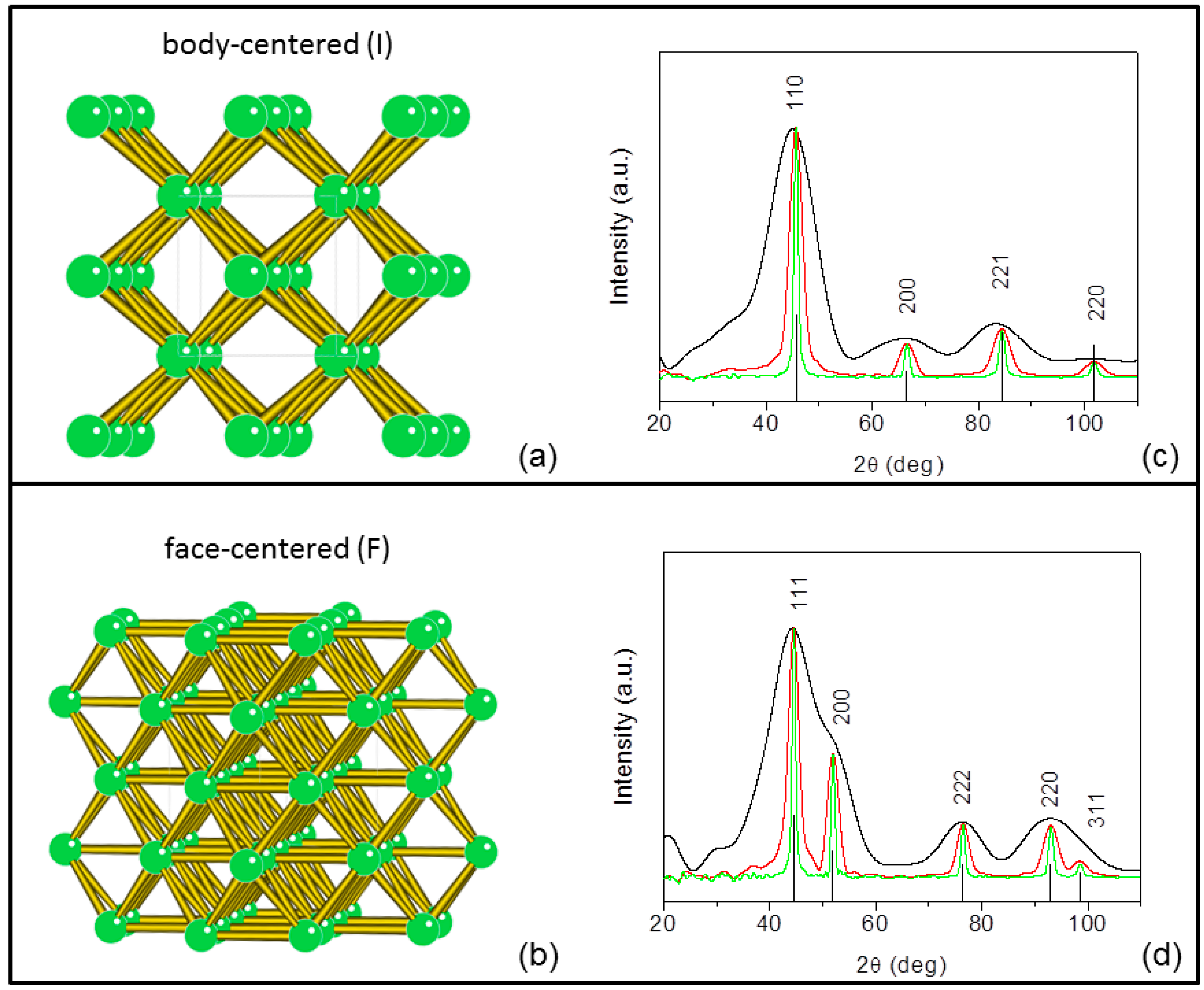
(SEM/TEM/HRTEM), atomic force microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photon spectroscopy, etc. This paper discusses the basic principle and applications of these instrumental techniques in the field of nanotechnology
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD Analysis) Powder XRD provides detailed information on the crystallographic structure and physical properties of materials and thin films. The sample is irradiated with a beam of monochromatic x-rays over a variable incident angle range. – x ray made easy pdf download Download X-ray diffraction is a useful and powerful analysis technique for characterizing crystalline materials commonly employed in MSE, physics, and chemistry.
X-ray diffraction analysis is the method by which multiple beams of x-ray create a three- dimensional picture of the density of electrons of any crystalline structure. The purpose is to
X-RAY DIFFRACTION RESIDUAL STRESS TECHNIQUES Paul S. Prevey Lambda Research INTRODUCTION In x-ray diff’raction residual strcss measurement, the Basic X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) • Diffraction from a crystal the Powder Diffraction File (PDF)
lohan de Villiers MODERN TECHNIQUES IN X-RAY DIFFRACTION-APPLIED TO METALLURGY Johan de Villiers Sabine Verryn University of Pretoria Abstract Through the application of the Rietveld method, X-ray diffraction analysis has developed into a fully quantitative method for phase analysis. The Rietveld method itself has progressed from an unstable method that required constant operator …
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is one of the most important non-destructive tools to analyse all kinds of matter – ranging from fluids, to powders and crystals. From research to production and engineering, XRD is an indispensible method for structural materials characterization and quality control which makes use of the Debye-Scherrer method. This technique uses X-ray (or neutron) diffraction on
Consequently, the X-ray diffraction pattern is the fingerprint . of periodic atomic arrangements in a given material. Diffraction patterns can be checked against large libraries of patterns from known materials in order to identify/quantify the phases present in a sample. COMMON APPLICATIONS While most other analytical techniques tend to provide elemental . or molecular information, XRD
X-ray diffraction is a popular technique to discover the structures of organic molecules such as proteins and, most famously, DNA , as well as inorganic crystals. It is also used to determine the degree of long-range order and symmetry present in a crystal, or lacking in a glass, which is the topic of the next module ( Session 21: Introduction to Glasses ).
background of X-ray diffraction techniques, the different types of equipment that can be used, practical issues relating to the specimen, the recommended measurement procedure and recommendations on how and what to record and report.
X-ray diffraction – Powder techniques – Phase analysis – Refinement of XRD data • Line profile analysis • Rietveld refinement • Neutron diffraction – Neutrons vs. X-ray. Fundamentals of diffraction • Transverse plane waves from different sources can “interfere” when their paths overlap • constructive interference (in phase) • destructive interference (out of phase
X-ray diffraction has been a standard technique for investigating structural properties of materials. However, most common applications in the organic materials community have been restricted to either chemical identification or qualitative strain analysis. Moreover, its use for polymeric thin films
X-ray Diffraction Techniques. What is crystallography? the study of macroscopic crystal forms “Crystal”: has been traditionally defined in terms of the structure and symmetry of these forms. Modern crystallography has been redefined by x-ray diffraction. By the study of atomic arrangements in crystalline materials The definition of a crystal has become that of Buerger (1956): “a region
X-RAY DIFFRACTION RESIDUAL STRESS TECHNIQUES Paul S. Prevey Lambda Research INTRODUCTION In x-ray diff’raction residual strcss measurement, the
X-Ray Diffraction In this technique, a sample is irradiated with x-rays and the intensity of the diffracted beams is measured as a function of scattering angle. X-ray diffraction techniques can be used for analysing powder and thin film specimens.
A Qualitative Study of Reactive Powder Concrete using X-Ray Diffraction Technique. www.iosrjen.org 13 P a g e
Diffraction Basics University of New Mexico
X-RAY DIFFRACTION RESIDUAL STRESS TECHNIQUES

Revisiting Powder X-ray Diffraction Technique A Powerful
X-Ray Diffraction Residual Stress Techniques

A Qualitative Study of Reactive Powder Concrete using X
X-Ray Diffraction Technique Applied to Study of Residual

X-ray Diffraction Techniques Ab Initio Structure
X-Ray Diffraction an overview ScienceDirect Topics
x wing miniatures rules pdf – X-Ray Diffraction Techniques meatscience.org
X-ray scattering techniques Wikipedia


XRay Crystallography Procedure and Instrumentation UCLA
18. X-Ray Diffraction Techniques Crystalline Materials
Comments
X-ray diffraction (XRD) can provide useful information about the composition of an ore sample in terms of quantification of crystalline phases and also amorphous content. XRD is also a powerful technique for studying substitutional solid solutions that can
X-Ray Diffraction Technique Applied to Study of Residual
X-RAY DIFFRACTION RESIDUAL STRESS TECHNIQUES
Revisiting Powder X-ray Diffraction Technique A Powerful
For example, X-ray spectroscopic technique using a standard crystal diffraction grating is very sensitive in the identification of trace elements; sensitivities of the order of 1 part in 10,000 have been claimed in modern applications to the study of rare earth minerals.
X-ray Diffraction Techniques
X-ray crystallography (XRC) is a technique used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X …
Determination of Residual Stresses by X-ray Diffraction
X-Ray Diffraction Technique for Residual Stress