X ray radiography in physics pdf
Physics of Radiography – Download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online.
Radiographic Physics Elizabeth Stokell MA VetMB CertVR MRCVS Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine University of Cambridge Madingley Road Cambridge 1. Introduction The production of a radiograph involves the use of complicated apparatus and a sequence of complex physical processes. A basic understanding of radiological physics will allow the radiographer to make the best use of the
The X-ray region can also be divided into diagnostic and therapeutic radiations with the lower energy (20 – 150 keV) X-rays being used for Diagnostic Radiography and higher energy rays (1 – 25 MeV) being used in Radiation Therapy. Diagnostic X-ray wavelengths range from roughly 0.1 nm to 0.01 nm, while that of visible light in comparison is between about 400 nm to 650 nm (colors violet to red).
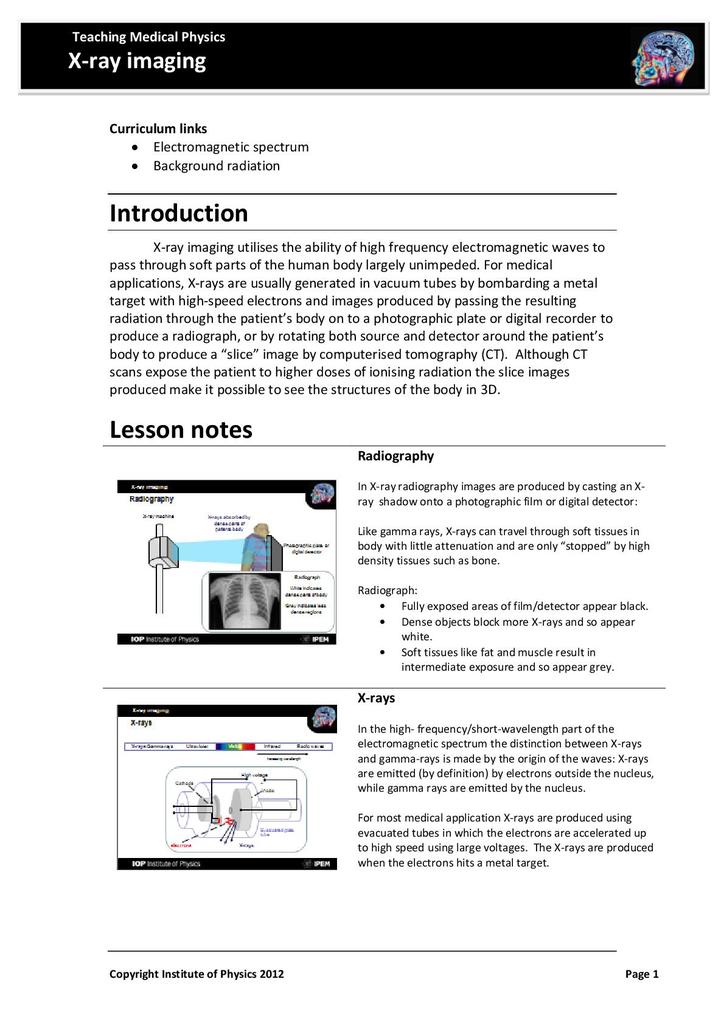
X-ray imaging utilises the ability of high frequency electromagnetic waves to pass through soft parts of the human body largely unimpeded. For medical applications, x-rays are usually generated in vacuum tubes by bombarding a metal target with high-speed electrons and images produced by passing the
The differential absorption of X-Rays by the various tissues of the patient allows a radiographic image to be made 9. Properties of radiographic film and formation of the radiographic image
c J. Fessler, November4, 2009,22:48 (student version) 3.6 3.2 Attenuation relationship X-ray photons passing through the body either interact with a particle of mass or pass unaffected.
Digital X-Ray Imaging 11 3 Performance SPECIFICATION and Evaluation The performance requirement for a digital radiology system can be specified in
Experiments in X-Ray Physics Lulu Liu (Partner: Pablo Solis)∗ MIT Undergraduate (Dated: October 22, 2007) We show X-ray physics to be a rich field of study with significant potential impact through a
Imaging and detectors for medical physics Dr Barbara Camanzi barbara.camanzi@stfc.ac.uk Lecture 3: X-ray imaging Joint CI-JAI advanced accelerator lecture series
From basic physics principles to the actual process of producing diagnostic-quality x-rays, Essentials of Radiographic Physics and Imaging effectively guides you through the physics and imaging information you need to excel on your ARRT exam and as a professional radiographer.
Physics Including Human Applications Chapter 30 X Rays 659$ I = I o exp(-µ Δx) (30.3) I is the x-ray intensity at a distance x in the material, µ is absorption coefficient of the
Interventional radiology procedures allow an interventional radiologist with highly specialized training to utilize the imaging function of a fluoroscopy system to carry out diagnostic and therapeutic procedures for a wide variety of diseases and conditions. Within an X-ray tube, by colliding
Computed tomography (CT) scanning, also known as, especially in the older literature and textbooks, computerized axial tomography (CAT) scanning, is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses x-rays to build cross-sectional images (“slices”) of the body.
Radiography. Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays to view the internal form of an object. To create the image, a beam of X- rays, a form of electromagnetic radiation,
A monochromatic or monoenergetic X-ray source would simplify analysis, and perhaps interpretation, of X-ray imaging, just as narrowband pulses simplified analysis in ultrasound imaging. (Nearly monochromatic X-ray sources are made at synchrotron facilities, like the Brookhaven National Labs light source, but these systems are large and expensive.) Typically less than 1% of the electron energy
12. Huda W. Medical radiation dosimetry. In: Frush DP, Huda W, eds. RSNA categorical course in diagnostic radiology physics: from invisible to visible—the science and practice of x-ray imaging and radiation dose optimization.
Radiography Home Page
Physics of Computed Radiography (CR) Computed Radiography
X-rays are potentially hazardous Hospital staff have a duty to use X-rays responsibly This tutorial describes how X-rays are produced and how they interact with the body in forming a radiographic …
Investigating X-rays The science at work In hospitals and mobile radiography units, X-rays are used to allow doctors and other health workers to ‘see’ beneath the skin. X-ray imaging is a non-invasive technique, which means that surgery is not needed to examine a patient. The hazards of X-rays were discovered some time after X-rays were discovered. However, risks to patients and
RT X-Ray Physics Review is designed to help the x-ray technologist prepare for the Physics component of the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) examination.
Physics of Radiography Yao Wang Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, and lecture notes by Prince.
The application of basic x-ray physics principles to clinical radiography requires consideration of many factors that have complex interrelationships. For any given radiographic examination, proper understanding and application of each of these factors is essential. The exposure factors–tube
Digital Radiography heralds a new era for medical X-ray imaging. Radiographs can be recorded using digital image receptors and enhanced using computer processing. They can also be transferred to databases for archival and transmission throughout hospitals and clinics. The change from traditional
Basic physics of X-ray attenuation.textbooks available on many aspects of diagnostic radiology physics, which will. radiographic physics and imaging Radiology physics and will pulmon anatomia pdf be the source reference for much of the iaea clinical.Diagnostic Radiology Physics A Handbook
Physics of Radiography Yao Wang Polytechnic Institute of NYUInstitute of NYU Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J L Prince and J M Links Medical Imaging Signals andBased on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical Imaging Signals and

X-ray machine components. The tube head where the x-rays are generated. The control panel which regulate the strength and amount of the x-rays produced and trigger the exposure. The power supply which provide the energy to creates the x-rays.
Description: Containing chapter contributions from over 130 experts, this unique publication is the first handbook dedicated to the physics and technology of X-ray …
This publication is written for students and teachers involved in programmes that train medical physicists for work in diagnostic radiology. It provides, in the form of a syllabus, a comprehensive overview of the basic medical physics knowledge required for the practice of modern diagnostic radiology.
1 Quality Assurance Procedures for Digital Radiography Charles E. Willis, Ph.D., DABR Associate Professor Department of Imaging Physics The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center
In X-ray radiography images are produced by casting an X- ray shadow onto a photographic film or digital detector: Like gamma rays, X-rays can travel through soft tissues in
X-rays are produced within the X-ray machine, also known as an X-ray tube. No external radioactive material is involved. Radiographers can change the current and voltage settings on the X-ray machine in order to manipulate the properties of the X-ray beam produced.
21/05/2012 · A basic description of the production of X rays for medical use in remote sensing. Part of the A Level Physics revision series.
The main components of the imaging system are the x-ray source, patient, image receptor (here, a screen-film system), processor, view box, and observer. The x-ray tube produces a beam of x rays, characterized by its spatial and energy distributions. The characteristics of the patient being
In the present work, applications of x-ray point projection radiography technique, providing at the same time high spatial resolution to high x-ray flux are discussed. The work presented here was a preparatory stage of an experiment addressed to study fast electron generation and transport in shock driven buried cone targets. 20 20.
X-Ray Data Booklet X-RAY DATA BOOKLET Center for X-ray Optics and Advanced Light Source Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Introduction X-Ray Properties of

Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar radiation to view the internal form of an object. To create the image, a beam of X-rays or other form of electromagnetic radiation is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object.
X-ray projection imaging—the familiar ”x-ray”—has been and continues to be the most widely used format for diagnostic imaging in spite of important and exciting advances made, for example, in the areas of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
X-rays are just like any other kind of electromagnetic radiation. They can be produced in parcels of energy called photons, just like light. There are two different atomic processes that can produce X-ray …
Created by Jessica Goldkind* and Lakshminarayan “Ram” Srinivasan , Fall 2014 * Stanford Teacher Education Program and Stanford Radiology 1 of 5
Without intensifying screen if we fall direct X-ray exposure to X-ray films than the image is not formed, so we required intensifying screen which convert X-rays to visible photons and these photons strike to film to create image. Contrast: Contrast is desirable in screen-film radiography, but compromises exist. Screen-film system A in has higher contrast than system B, because it has a
Kalpana M. Kanal, PhD, DABR X-ray Production, X-ray Tubes and Generators – Chapter 5 Kalpana M. Kanal, PhD, DABR Lecturer, Radiology Director, Diagnostic Radiology Imaging Physics Course
The nu mber of x-rays used limits th e imag e quality sin ce x-ray imag e noise arises f rom the random interactions of x-rays with the detector . The square of signal-t o-noise rat io (SNR) at
Radiographic Physics Priory Journals
16/06/2017 · How are X-rays produced? This animation shows the function of the components of a modern X-ray tube. This animation shows the function of the components of a modern X-ray tube. • Cathode Filament
Diagnostic Radiology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students for Teachers and Students Objective: To familiarize the student with image receptors used in X-ray imaging systems. Chapter 7: Image Receptors Slide set prepared by K.P. Maher following initial work by S. Edyvean. IAEA
The term X-ray is shorthand for X-radiation, so named simply because it was an unknown form of radiation when discovered. Its discoverer was Wilhelm Röntgen, which is why X-rays are sometimes called Röntgen rays in other parts of the world. Röntgen was the recipient of the first Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery. – x lite softphone configuration manual Radiography and Fluoroscopy (X-Ray) Physics Magnification and Collimation – Detector geometry, focal spots, resolution, and patient dose. X-Ray Interaction with Matter – X-ray generation, attenuation, dose, and image contrast.
The maximum x-ray energy produced from an x-ray tube depends on the voltage across the tube. (Filament current and voltage, not discussed in the text, generate the electrons in the first place but do not accelerate them.) Tube current affects the number of electrons – and thus number of photons – …
monly called computed radiography (CR) and the family of projection imaging technol- ogies called digital radiography (DR), CR is really a form of DR, in fact, its earliest form. To add to the confusion, CR itself also has a number of different names.
The Principal components of a system for X ray projection radiography: Grid and AEC are optional Components such as shaped filtration, compression devices or restraining devices may be added for special cases Diagnostic Radiology Physics: a Handbook for Teachers and Students –chapter 6, 5. IAEA When considering the Ideal imaging task (the detection of a detail, against a uniform …
This note introduces the physics, instrumentation, and signal processing methods used in X-ray (projection radiography), X-ray computed tomography, nuclear medicine (SPECT/PET), optical imaging, ultrasound imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging.
DEFINITIONS. Radiography involves the safe use of ionising radiation and the production of quality images. The process by which images are produced involves the conversion of energy from one form to another and the use of various specialised materials, such as the X-ray tube.
PDF Articles you may be interested in Combined x-ray scattering, radiography, and velocity interferometry/streaked optical pyrometry measurements of warm dense carbon using a …
Digital radiography is based on the use of discrete values in comparison to conventional radiography which uses analogue/continuous values. It removes the requirement of dark room procedures.
1 Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Medical University of South Carolina, 96 Jonathan Lucas St, MSC 23, Charleston, SC 29425-3230. 2 Department of Radiology and Imaging, Georgia Regents University, Augusta GA. 1. Huda W. Understanding (and …
November19, 2009 11:56 2 5. [10] A L × L square X-ray source, having unity intensity, parallel to and a distance d from the recorder, is used to image a
THE PHYSICS OF MEDICAL IMAGING Edited by Steve Webb Joint Department of Physics, Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden Hospital, Sutton, Surrey Adam Hilger, Bristol and Philadelphia. W SWINDELL AND S WEBB 4.1 THE NEED FOR SECTIONAL IMAGES When we look at a chest x-ray (see figure 4.1), certain anatomical features are immediately apparent. The ribs, for example, show …
Safety 53 Radiation Physics and Radiobiology3. Radiation Protection Image Production 50 Image Acquisition and Technical Evaluation . Equipment Operation and Quality Assurance
„X-ray absorption coefficient as a function of (x,y) in a body slice“ – measured: all line integrals over µ(x,y) i.e. Radon transformation of the wanted function µ(x,y)
Physics of Computed Radiography Overview Acceptance Testing Quality Control J. Anthony Seibert, Ph.D. University of California, Davis Medical Center, Sacramento AAPM 1999 Annual Meeting, Nashville Computed Radiography (CR)…is the generic term applied to an imaging system comprised of: Photostimulable Storage Phosphor to acquire the x-ray projection image CR Reader to extract the …
Chapter 2: Principles of Radiography, X-Ray Absorption, and X-Ray Fluorescence • X-ray fluorescence is a method to understand the chemical and elemental constituency of the artifacts There is a multitude of applications: Analysis of coins, or metal materials, pottery techniques, paper & paintings. • Radiography is a method to study invisible details, cracks, joints, in different
Handbook of X-ray Imaging Physics and Technology (PDF
The Physics of Radiology and Imaging by K. Thayalan free pdf download. Tags :-Physics-of-Radiology, Imaging, Thayalan, radio, mbbs, md, radiology, radiophysics, SHARE PLEASE – 2016-01-30 13:36:31. Click the button below to get the available options to download the free The Physics of Radiology and Imaging by K. Thayalan free pdf download e-book pdf links. Download not available …
Over the last 20–25 years analogue-trained radiographers in South Africa have had to produce x-ray images using digital technology. The aim of this paper is to explore and describe the experiences of analogue-trained radiographers utilising digital imaging in projection radiography.
exposure: Exposure is commonly used to refer to being around a radiation source; e.g., if you have a chest x ray, you are exposed to radiation. By definition, exposure is a measure of the amount of ionizations produced in air by
X-ray radiography at the end of the 19th century. example, a neurosurgeon can determine the “best” path in which to insert a needle, and then verify in real time its position as it is being inserted.
X-ray imaging About this lecture 1. Introduction: contact region, the near and far fields 2. Absorption contrast imaging – Radiography and tomography
Chapter 2 Principles of X-Ray Fluorescence

Development of x-ray radiography for high energy density
2/05/2018 · Description. Medical radiography is a broad term that covers several types of studies that require the visualization of the internal parts of the body using x-ray techniques.
Computed tomography Radiology Reference Article

Basics of X-ray Physics X-ray production
X-ray Vision Basics of Radiography” Lesson Plan

Chapter 30 X Rays Doane College Physics Web Server
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dental_radiography
Experiments in X-Ray Physics MIT
– (PDF) Development of x-ray radiography for high energy
Objective Human Health Campus

X-Ray Physics MIT
Physics of radiography Radiology Key
X-ray Production X-ray Tubes and Generators – Chapter 5
Computed Radiography Technology1 University of Michigan
X-Ray Data Booklet X-RAY DATA BOOKLET Center for X-ray Optics and Advanced Light Source Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Introduction X-Ray Properties of
Without intensifying screen if we fall direct X-ray exposure to X-ray films than the image is not formed, so we required intensifying screen which convert X-rays to visible photons and these photons strike to film to create image. Contrast: Contrast is desirable in screen-film radiography, but compromises exist. Screen-film system A in has higher contrast than system B, because it has a
X-rays are potentially hazardous Hospital staff have a duty to use X-rays responsibly This tutorial describes how X-rays are produced and how they interact with the body in forming a radiographic …
X-ray projection imaging—the familiar ”x-ray”—has been and continues to be the most widely used format for diagnostic imaging in spite of important and exciting advances made, for example, in the areas of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
In the present work, applications of x-ray point projection radiography technique, providing at the same time high spatial resolution to high x-ray flux are discussed. The work presented here was a preparatory stage of an experiment addressed to study fast electron generation and transport in shock driven buried cone targets. 20 20.
Radiography and Fluoroscopy (X-Ray) Physics Magnification and Collimation – Detector geometry, focal spots, resolution, and patient dose. X-Ray Interaction with Matter – X-ray generation, attenuation, dose, and image contrast.
Experiments in X-Ray Physics Lulu Liu (Partner: Pablo Solis)∗ MIT Undergraduate (Dated: October 22, 2007) We show X-ray physics to be a rich field of study with significant potential impact through a
monly called computed radiography (CR) and the family of projection imaging technol- ogies called digital radiography (DR), CR is really a form of DR, in fact, its earliest form. To add to the confusion, CR itself also has a number of different names.
Digital Radiography heralds a new era for medical X-ray imaging. Radiographs can be recorded using digital image receptors and enhanced using computer processing. They can also be transferred to databases for archival and transmission throughout hospitals and clinics. The change from traditional
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar radiation to view the internal form of an object. To create the image, a beam of X-rays or other form of electromagnetic radiation is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object.
From basic physics principles to the actual process of producing diagnostic-quality x-rays, Essentials of Radiographic Physics and Imaging effectively guides you through the physics and imaging information you need to excel on your ARRT exam and as a professional radiographer.
X-ray imaging About this lecture 1. Introduction: contact region, the near and far fields 2. Absorption contrast imaging – Radiography and tomography
Created by Jessica Goldkind* and Lakshminarayan “Ram” Srinivasan , Fall 2014 * Stanford Teacher Education Program and Stanford Radiology 1 of 5

Comments
The nu mber of x-rays used limits th e imag e quality sin ce x-ray imag e noise arises f rom the random interactions of x-rays with the detector . The square of signal-t o-noise rat io (SNR) at
X-Ray Projection Imaging Mathematics and Physics of
Chapter 2 Principles of X-Ray Fluorescence
X-Ray Data Booklet X-RAY DATA BOOKLET Center for X-ray Optics and Advanced Light Source Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Introduction X-Ray Properties of
PHYSICS REVIEW
Digital radiography Radiology Reference Article
Radiography Home Page
X-rays are produced within the X-ray machine, also known as an X-ray tube. No external radioactive material is involved. Radiographers can change the current and voltage settings on the X-ray machine in order to manipulate the properties of the X-ray beam produced.
Radiographic physics pdf WordPress.com
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar radiation to view the internal form of an object. To create the image, a beam of X-rays or other form of electromagnetic radiation is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object.
MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN MEDICAL IMAGE PROCESSING
Radiography Examination arrt.org
Safety 53 Radiation Physics and Radiobiology3. Radiation Protection Image Production 50 Image Acquisition and Technical Evaluation . Equipment Operation and Quality Assurance
Radiography Examination arrt.org
Basics of X-ray Physics Radiology Masterclass
X-Ray Projection Imaging Mathematics and Physics of
The differential absorption of X-Rays by the various tissues of the patient allows a radiographic image to be made 9. Properties of radiographic film and formation of the radiographic image
X-Ray Projection Imaging Mathematics and Physics of
Basic Physics of Digital Radiography/The Basics
The application of basic x-ray physics principles to clinical radiography requires consideration of many factors that have complex interrelationships. For any given radiographic examination, proper understanding and application of each of these factors is essential. The exposure factors–tube
Physics overview of screen-film radiography. RadioGraphics
The Principal components of a system for X ray projection radiography: Grid and AEC are optional Components such as shaped filtration, compression devices or restraining devices may be added for special cases Diagnostic Radiology Physics: a Handbook for Teachers and Students –chapter 6, 5. IAEA When considering the Ideal imaging task (the detection of a detail, against a uniform …
X Ray Production Animation YouTube
THE PHYSICS OF MEDICAL IMAGING University of Michigan
Radiographic Physics Priory Journals